1 Chromatid Chromosom

Zwei Chromatid Chromosom Biologie Lehrbuch Biologie Abitur
How Many Dna Molecules And Genes Does A Single Chromosome Contain Quora

Chromatid Wikipedia
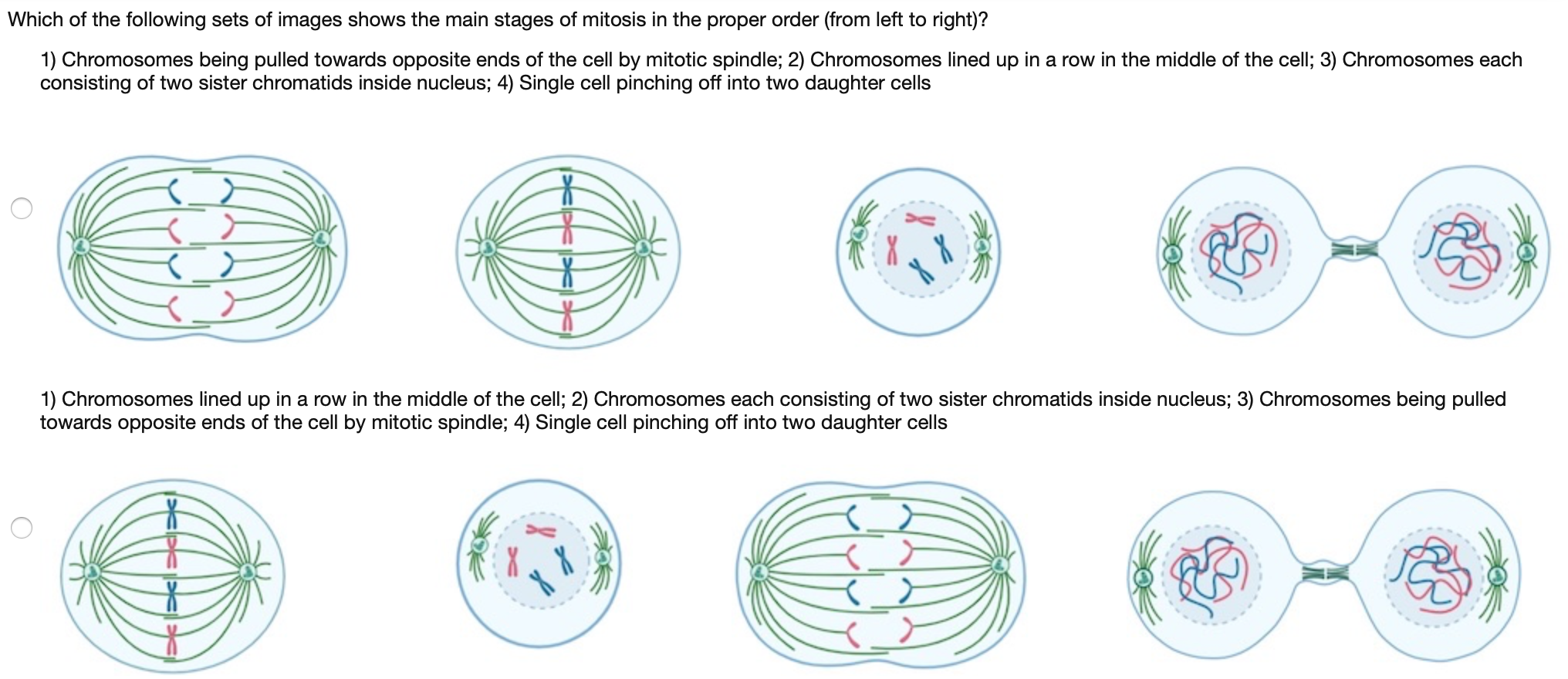
Solved Which Of The Following Sets Of Images Shows The Ma Chegg Com

Chromosomen Und Chromatin Theoretisches Material Biologie 12 Schulstufe

What Is A Chromosome Biology Stack Exchange
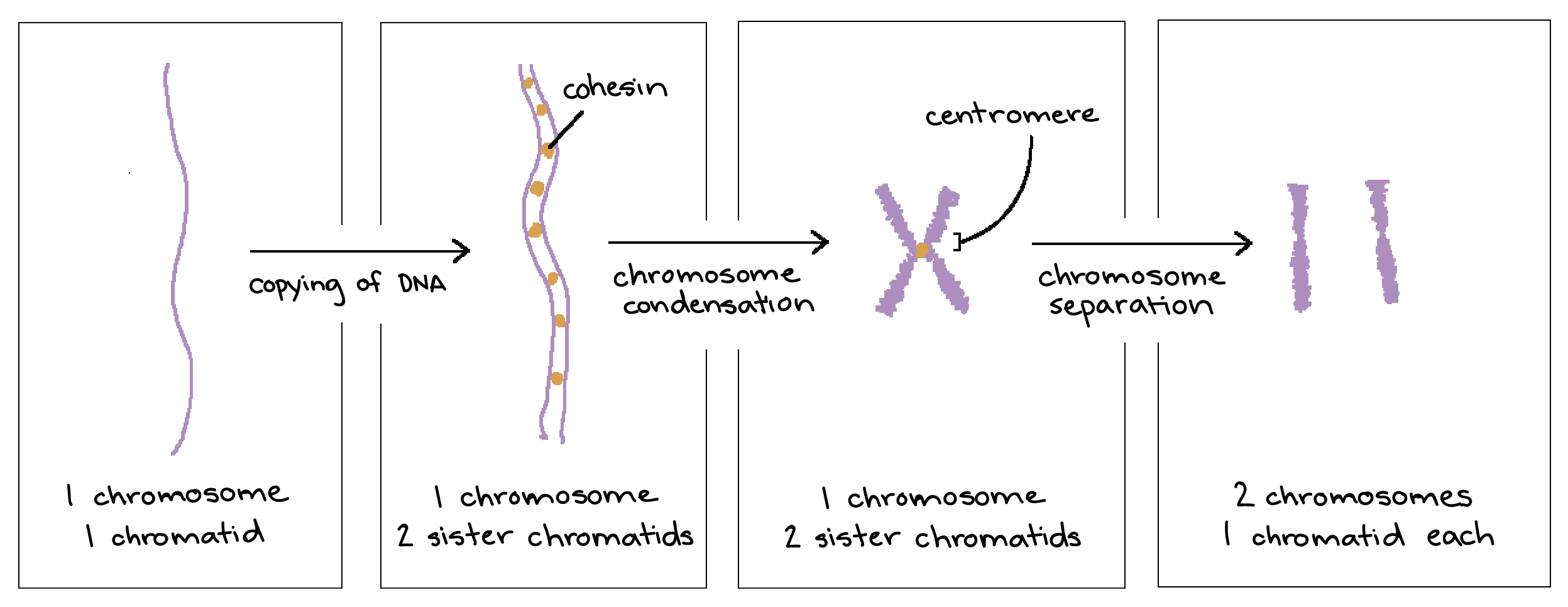
A chromatid is one half of a replicated chromosomePrior to cell division, chromosomes are copied and identical chromosome copies join together at their centromeresEach strand of one of these chromosomes is a chromatid Joined chromatids are known as sister chromatids.

1 chromatid chromosom. O Chromosome # 46 o Chromatid # 46 End of meiosis II (in daughter cells) o Cell = n haploid o Chromosome # 23 o Chromatid # 23 Meiosis is reduction division that occurs only in germ cells where gametes are produced with half the chromosome number to that of the parent cellGametes are always haploid Gametes should be haploid for. A chromatid (Greek khrōmat 'color' id) is one copy of a newly copied chromosome which is still joined to the original chromosome by a single centromere Before replication, one chromosome is composed of one DNA molecule Following replication, each chromosome is composed of two DNA molecules;. They usually have the same genes at the same relative locations.
A chromatid (Greek khrōmat'color' id) is one half of a duplicated chromosome In the diagram, (1) refers to a chromatid 1half of two identical threadlike strands of a replicated chromosome During cell division, the identical copies (called a " sister chromatid pair ") are joined at the region called the centromere (2). They are then called sister chromatids since they are identical to each other. In the image above, what lettered section represents 2 chromosomes, each with 1 chromatid?.
A chromatid is one of two identical copies of DNA making up a chromosome that are joined at their centromeres, for the process of nuclear division (mitosis or meiosis)The term is used so long as the centromeres remain in contact When they separate (during anaphase of mitosis and anaphase 2 of meiosis), the strands are called daughterchromosomesThe tips of the chromatid are called telomeres. A chromosome is a string of DNA that is unique to the human having this chromosome A string of DNA in the cell nucleus is also called a chromatid, So a chromosome and a chromatid is the same The difference is most often whether the string of DNA. Each chromosome is made of 2 chromatids which are identical in gene position So the chromosome from the male will have 2 male chromatids and the female chromosome will have 2 female chromatids.
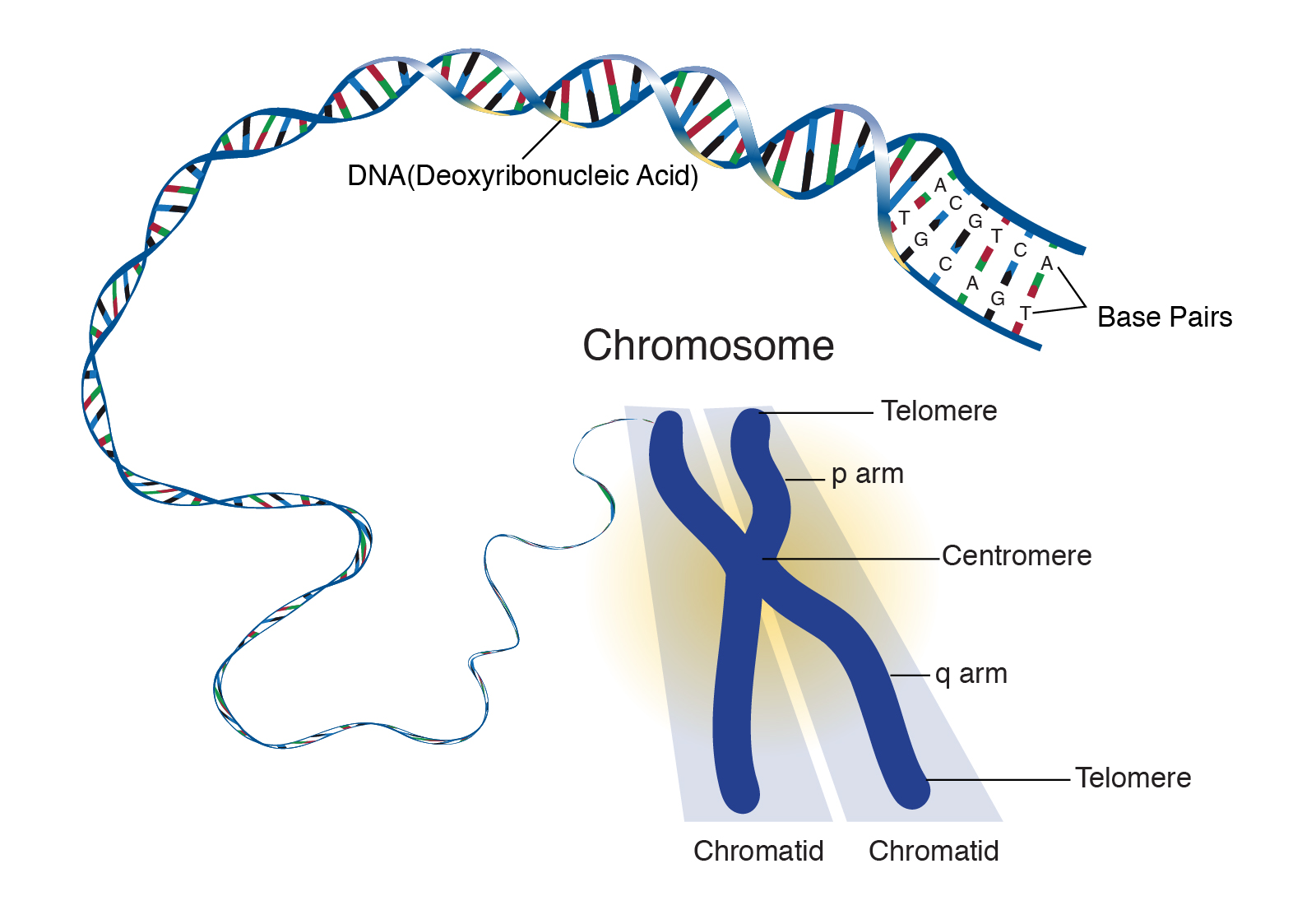
60 Which of the following statements are true about the homologous chromosomes of a pair?. Other articles where Chromatid is discussed centromere that holds together the two chromatids (the daughter strands of a replicated chromosome) The centromere is the point of attachment of the kinetochore, a structure to which the microtubules of the mitotic spindle become anchored The spindle is the structure that pulls the chromatids to opposite ends of the cell. Diagram o a replicatit an condensed metaphase eukaryotic chromosome (1) Chromatid – ane o the twa identical pairts o the chromosome efter S phase (2) Centromere – the pynt whaur the twa chromatids titch (3) Short (p) airm (4) Lang (q) airm A chromosome (frae auncient Greek χρωμόσωμα,.
Chromatid Definition When a cell is preparing to divide, it makes a new copy of all of its DNA, so that the cell now possesses two copies of each chromosome The two copies of the cell’s original chromosome are called “sister chromatids” During anaphase of cell division, the two chromatids will be pulled apart, and chromatid will be apportioned to the cytoplasm of each daughter cell. Bei 448 ist ein Fehler Ein Nukleosom besteht aus DNA plus dem Histonenkomplex Der Histonenkomplex besteht aus 8 Histonen Sorry!WERDE EINSER. Each chromatid thus becomes a fullfledged chromosome • The two liberated daughter chromosomes begin moving toward opposite ends of the cell as their kinetochore miclOtubules shorten Because these microtubules are anached at the centromere region, the chromosomes move centromere first (at about 1 f1m1min).
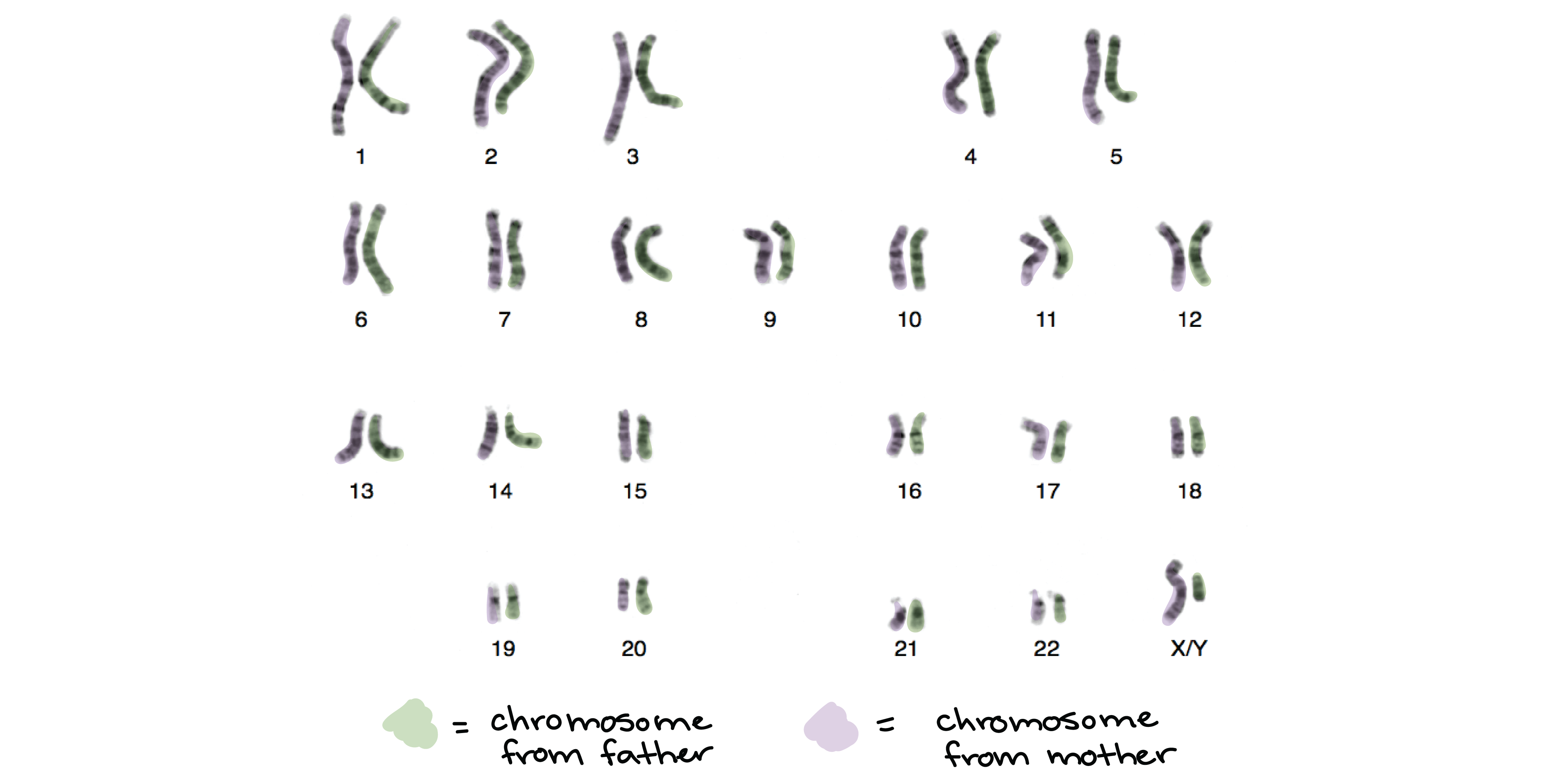
Figure 5 Up to now the images have been designed to illustrate one chromosome either individually, as an homologous pair or as a pair of sister chromatids But of course most organisms have more than one chromosome Leaving aside the X and Y chromosomes your cells have 22 pairs of homologous chromosomes or 44 individual chromosomes When these. Autosomes are labeled 122 for reference Each chromosome pair consists of one chromosome inherited from the mother and one from the father In addition to the 22 numbered autosomes, humans also. The paternal (blue) chromosome and the maternal (pink) chromosome are homologous chromosomes Following chromosomal DNA replication, the blue chromosome is composed of two identical sister chromatids and the pink chromosome is composed of two identical sister chromatids In mitosis, the sister chromatids separate into the daughter cells, but are now referred to as chromosomes (rather than chromatids) much in the way that one child is not referred to as a single twin.
1 Definition Ein EinChromatidChromosom ist ein Chromosom, das nur aus einem Chromatid besteht 2 Hintergrund Zu Beginn der Anaphase einer Mitose oder der Anaphase II der Meiose entsteht es aus dem ZweiChromatidChromosomIn der Interphase wird dieses EinChromatidChromosom durch DNAReplikation wieder in ein ZweiChromatidChromosom umgewandelt. A chromatid is just 1 copy of the freshly duplicated chromosome that is nevertheless connected into this completely different backup with one particular centromere Earlier replication, inch chromosome is composed of only 1 DNA molecule. The commonly seen chromosome “X” shape only exists immediately after chromosome replication, and consists of the original chromosome, attached to its “sister” chromatid (identical, if all went according to RNA plans) So the answer you’re looking.
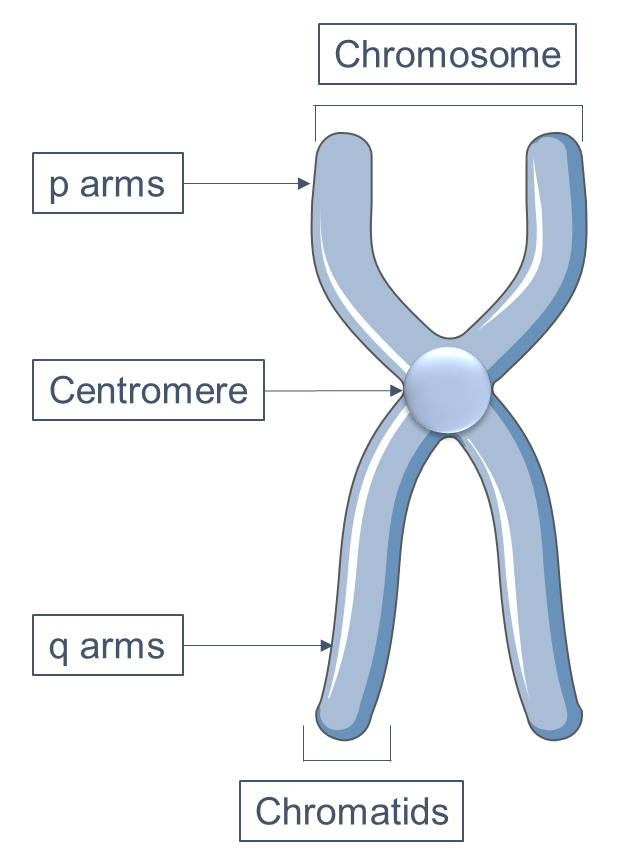
In the image above, what lettered section represents 2 chromosomes, each with 1 chromatid?. English Scheme of a Chromosome (1) Chromatid One of the two identical parts of the chromosome after S phase (2) Centromere The point where the two chromatids touch, and where the microtubules attach (3) Short (p) arm (4) Long (q) arm In accordance with the display rules in Cytogenetics, the short arm is on top. Chromosomes,chromatids, centromeres and telomeres;.
English Scheme of a Chromosome (1) Chromatid One of the two identical parts of the chromosome after S phase (2) Centromere The point where the two chromatids touch, and where the microtubules attach (3) Short (p) arm (4) Long (q) arm In accordance with the display rules in Cytogenetics, the short arm is on top. Combining the differences and the similarities, we can conclude that a chromatid is always a part of a chromosome while the chromosome is made of DNA and proteins The main difference between a chromosome and a chromatid is in the level of condensation While DNA is condensed 10,000 times in a chromosome, it is condensed 50 times in a chromatid. Chromatid exchanges may also occur between two arms of the same chromosome or between two different sites on the same chromosome arm such intrachromosomal exchanges are called chromatid intrachanges(Fig 2) Catcheside et al (1946a) distinguished the two‐arm and one‐arm classes as interarm intrachanges and intra‐arm intrachanges (It is not necessary to memorize all this terminology.
A) Chromosome and chromatid b) Centrosome and centromere c) Aster and spindle fibres d) Haploid and diploid Solution 1 (a) A chromosome is an organized structure of DNA and protein found in cells It is a single piece of coiled DNA containing many genes, regulatory elements and other nucleotide sequences whereas a chromatid is one of the. In the diagram, (1) refers to a chromatid 1half of two identical threadlike strands of a replicated chromosomeDuring cell division, the identical copies (called a "sister chromatid pair") are joined at the region called the centromere (2)Once the paired sister chromatids have separated from one another (in the anaphase of mitosis) each is known as a daughter chromosome. O Chromosome # 23 o Chromatid # 23 Meiosis is reduction division that occurs only in germ cells where gametes are produced with half the chromosome number to that of the parent cellGametes are always haploid Gametes should be haploid for maintaining the chromosome number of the species.
The important parts of a chromatid are;. Dietzel65 via Wikimediaorg) The process in which the nucleus of a eukaryotic cell divides is called mitosis During mitosis, the two sister chromatids that make up each chromosome separate from each other and move to opposite poles of the cell This is shown in the figure below. Chromatid In eukaryotes, DNA is found in chromosomes in the nucleus Chromosomes are made of a single molecule of DNA and proteins Chromosomes are linear, and DNA in them is double stranded There are many chromosomes in a single nucleus In prokaryotes, a single DNA molecule which is double stranded forms the chromosome.
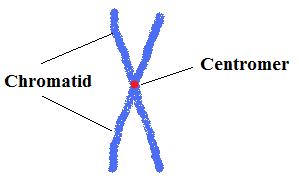
By definition, a chromatid is one of the two identical components that make up a duplicated chromosome As such, the chromosome is said to be compose of the identical sister chromatids Chromatids (sister) are formed after the chromatin condenses during metaphase. G 1 Phase (First Gap) The first stage of interphase is called the G 1 phase (first gap) because, from a microscopic aspect, little change is visible However, during the G 1 stage, the cell is quite active at the biochemical level The cell is accumulating the building blocks of chromosomal DNA and the associated proteins as well as accumulating sufficient energy reserves to complete the task. One chromosome contains two similar structures that are held together at a point called the centromere Each of this is referred to as chromatid Hence, one chromosome has two chromatids that are connected by a centromere Chromosomes, therefore, possess an X shape The study of cell division and chromosomes is referred to as cytogenetics.
Chromatid definition is one of the usually paired and parallel strands of a duplicated chromosome joined by a single centromere. The important parts of a chromatid are;. The Chromatid Is a copy of a chromosome that remains attached to the original copy by an area of the chromosome called the centromere In this sense, the Chromatid Is a rodlike structure, known as an arm, which always, under normal conditions, will be united with its sister chromatid by the centromere The Chromatids Exist during certain phases of a biological process known as mitosis, in.
Chromatid 1 Each chromosome consists of two symmetrical strands called chromatids, formed during Sphase 2 Each chromatid is half of the metaphase chromosome Anaphase chromosomes have only one chromatid, due to the splitting of centromere, which becomes the chromosome. A chromatid is one of two identical halves of a replicated chromosome During cell division, the chromosomes first replicate so that each daughter cell receives a complete set of chromosomes Following DNA replication, the chromosome consists of two identical structures called sister chromatids, which are joined at the centromere. Main Difference The main difference between sister chromatids and nonsister chromatid is that sister chromatid discusses the identical copies form by the DNA replication of a chromosome when both copies join together by a common centromere whereas nonsister chromatid refers to either one of the two chromatids of pair homologous chromosomes.
Section D How many chromosomes are in a yak's diploid cells?. Combining the differences and the similarities, we can conclude that a chromatid is always a part of a chromosome while the chromosome is made of DNA and proteins The main difference between a chromosome and a chromatid is in the level of condensation While DNA is condensed 10,000 times in a chromosome, it is condensed 50 times in a chromatid. Define chromatid chromatid synonyms, chromatid pronunciation, chromatid translation, English dictionary definition of chromatid n Either of the two daughter strands of a replicated chromosome that are joined by a single centromere and separate during cell division to become.
60 Which of the following statements are true about the homologous chromosomes of a pair?. Chromosome vs Chromatid Chromosomes are the threadlike structures that form the DNA molecule, whereas either of the two strands formed when a chromosome duplicates itself as part of the early stages of cell division is known as chromatid When we talk about the pair of chromosomes, we refer to the presence of the two chromatids. Each chromosome consists of two identical chromatids The image above represents a haploid (n) cell from a swamp wallaby There are no homologous pairs of chromosomes in the cell/The diploid (2n) number of this cell is 10 (2n=10) In the image above, what lettered section(s) represents 1 chromosome with 2 sister chromatids?.
Section D How many chromosomes are in a yak's diploid cells?. 1) Telomere Telomeres are short tandem repeats of nucleotides at the ends of chromosomes As DNA is sticky, Telomeres prevent one chromosome from binding to another 2) Short arm and long arm The short arm of a human chromosome is symbolized by convention as “p” The “p” symbol is from the. O Chromosome # 23 o Chromatid # 23 Meiosis is reduction division that occurs only in germ cells where gametes are produced with half the chromosome number to that of the parent cellGametes are always haploid Gametes should be haploid for maintaining the chromosome number of the species.
Diagram of a duplicated and condensed metaphase eukaryotic chromosome (1) Chromatid – one of the two parts of the chromosome after duplication (2) Centromere – the point where the two chromatids touch (3) Short arm (4) Long arm. A chromosome is a string of DNA that is unique to the human having this chromosome A string of DNA in the cell nucleus is also called a chromatid, So a chromosome and a chromatid is the same The difference is most often whether the string of DNA. Chromatid is the name of each copy of the chromosome after the S (synthesis) phase According to that terminology, there is no chromatid before the duplication I have to confess that I personally don't follow that terminology I like to say to my students that, before S phase, each chromosome has 1 chromatid and, after the S phase, each.
Chromatid is one of the two similar copies of DNA that makes up a single chromosome One chromosome has two chromatids joined by a centromere During the cell division (meiosis and mitosis), they are separated from each other;. Definition of chromatid in the Definitionsnet dictionary Meaning of chromatid What does chromatid mean?. Each chromatid thus becomes a fullfledged chromosome • The two liberated daughter chromosomes begin moving toward opposite ends of the cell as their kinetochore miclOtubules shorten Because these microtubules are anached at the centromere region, the chromosomes move centromere first (at about 1 f1m1min).
Chromatin is a substance that helps the formation of chromosomes and is composed of DNA, RNA (Nucleic Acid) and Proteins, being found in the nucleus of each cell representing approximately, two meters of DNA molecule of compact form. Chromatid Definition When a cell is preparing to divide, it makes a new copy of all of its DNA, so that the cell now possesses two copies of each chromosome The two copies of the cell’s original chromosome are called “sister chromatids” During anaphase of cell division, the two chromatids will be pulled apart, and chromatid will be apportioned to the cytoplasm of each daughter cell. In other words, DNA replication its.
How are chromatin, chromatid and chromosomes related to each other?. A sister chromatid refers to the identical copies formed by the DNA replication of a chromosome, with both copies joined together by a common centromereIn other words, a sister chromatid may also be said to be 'onehalf' of the duplicated chromosome A pair of sister chromatids is called a dyad. 2n 2c means two homolog (diploid) unreplicated chromosomes (two chromatids) 1n 1c one single chromosome (haploid) that is unreplicated 2n 4c Two homolog chromosomes (diploid) consisting each of two sister chromatids (two yellow and two blue), thus 4c in total 1n 2c one single chromosome in which DNA has been duplicated.
There are 23 pairs of chromosomes in humans Chromatid in a nutshell The chromatid appears during interphase, attached to the centromere and makes a chromosome It is made up of a network of chromatins A cytological assay known as sister chromatid exchange study helps to find out alterations and translocations between two chromatids. They usually have the same genes at the same relative locations. Basis for Comparison Chromosome Chromatid Definition A chromosome is a threadlike structure present in the nucleus or nuclear region of the cytoplasm that is made up of a single molecule of DNA and proteins, carrying some or all genetic materials of an organism.
Information and translations of chromatid in the most comprehensive dictionary definitions resource on the web. 1 The apparent chromatid and isochromatid breaks which we see at mitosis are the only direct evidence we have for supposing that radiation causes chromatid breakage where it has not caused chromatid exchange However, the experimental results reviewed in Section IV, B accord with the theory that all chromatid and isochromatid breaks are at sites of chromatid intrachange. 1 Chromatid, 2 Centromere, 3 short arm, 4 long arm (CC BYSA 30;.
Of two identical replicas, called chromatids, joined at a point called the centromere During mitosis the sister chromatids separate, one going to each daughter cell Chromosomes thus meet the first criterion for being the repository of genes they are replicated, and a full copy is passed to each daughter cell Read More;.
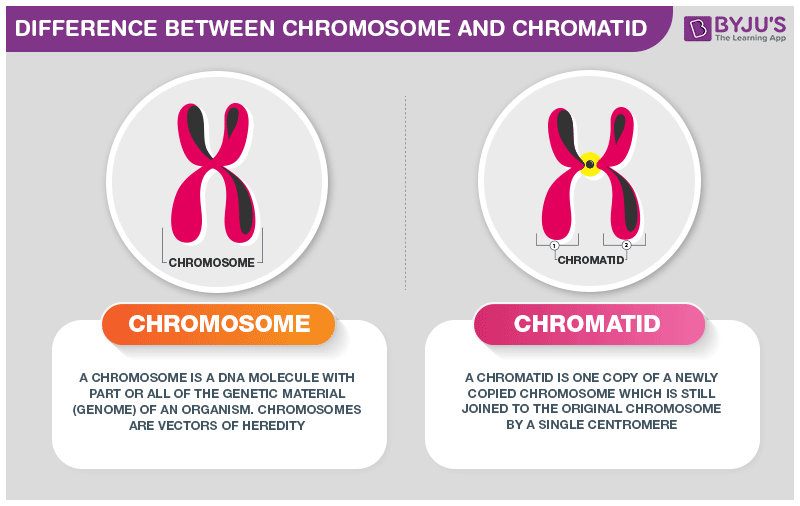
What Is The Difference Between Chromosome And Chromatid
Q Tbn And9gcrjxjt5rqddy9bwa3atzlnxslaruduwuktrorak6bikyucrijew Usqp Cau

The Cell Cycle Mitosis And Meiosis University Of Leicester
/homologous-chromosomes-with-annotations--764793193-5c43e02fc9e77c00018e6540.jpg)
What Is A Chromatid
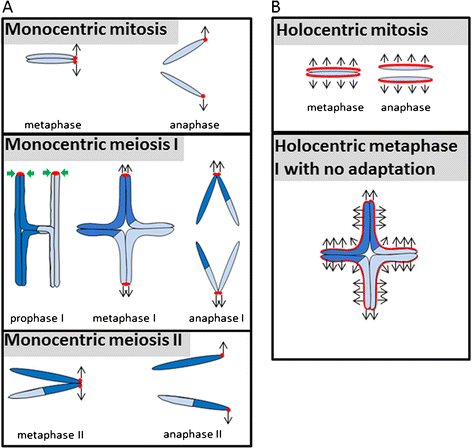
Holocentric Chromosomes Convergent Evolution Meiotic Adaptations And Genomic Analysis Springerlink
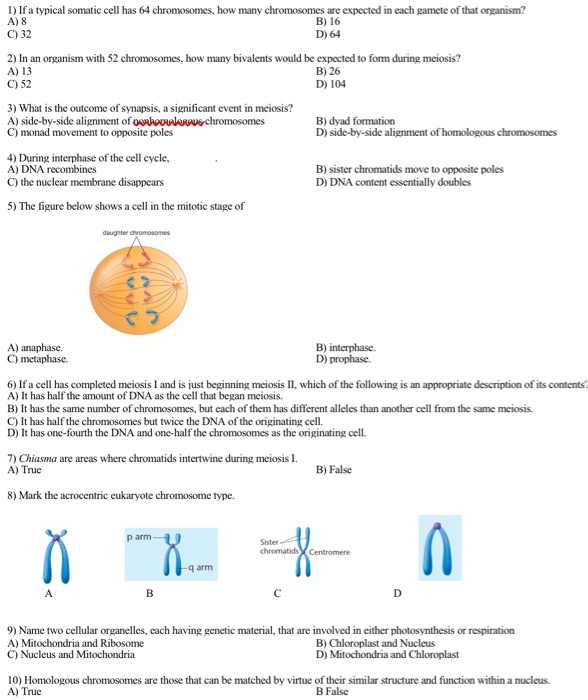
Solved A 8 1 If A Typical Somatic Cell Has 64 Chromosom Chegg Com

The Process Of Meiosis Biology I

What Is A Chromosome Biology Stack Exchange
Chromosome Structure And Numbers Review Article Khan Academy

Biology 2c03 Lecture Notes Fall 17 Lecture 2 Sister Chromatids Walther Flemming Homologous Chromosome
Chromosome
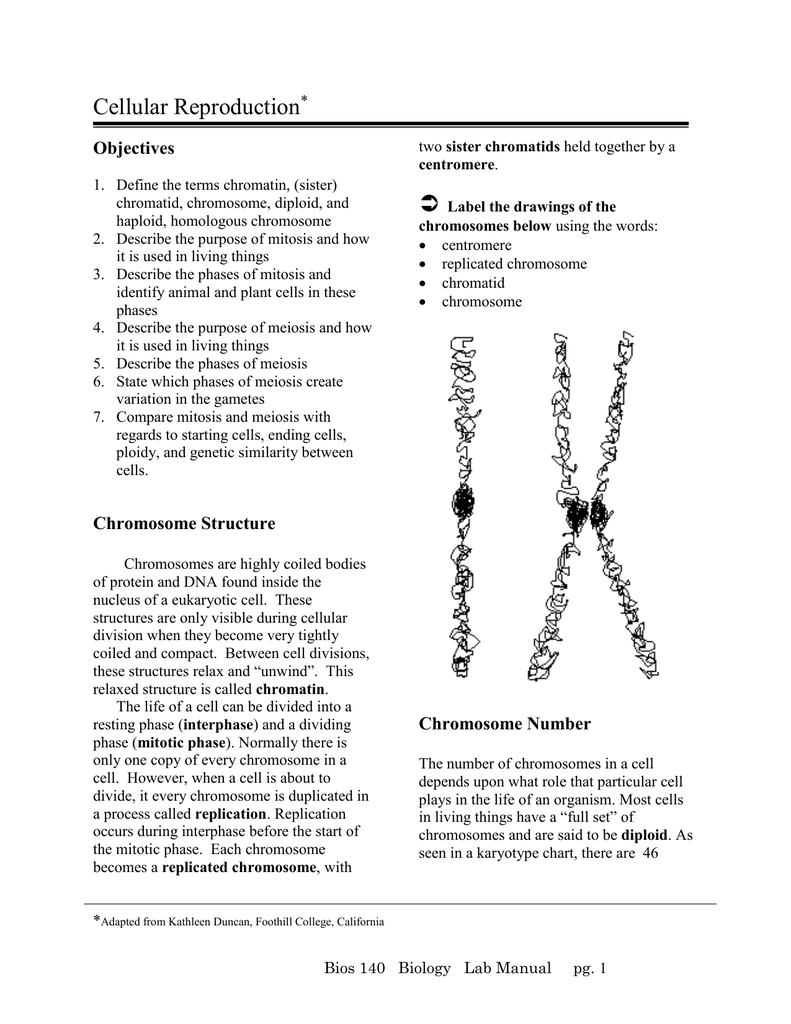
Cellular Reproduction Objectives
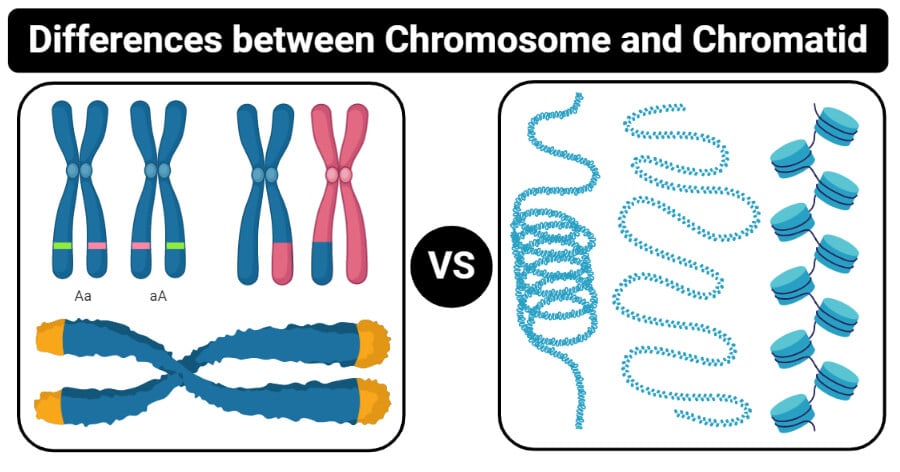
Chromosome Vs Chromatid Definition 11 Major Differences Examples

What Are Chromosomes Easy Exam Revision Notes For Gsce Biology
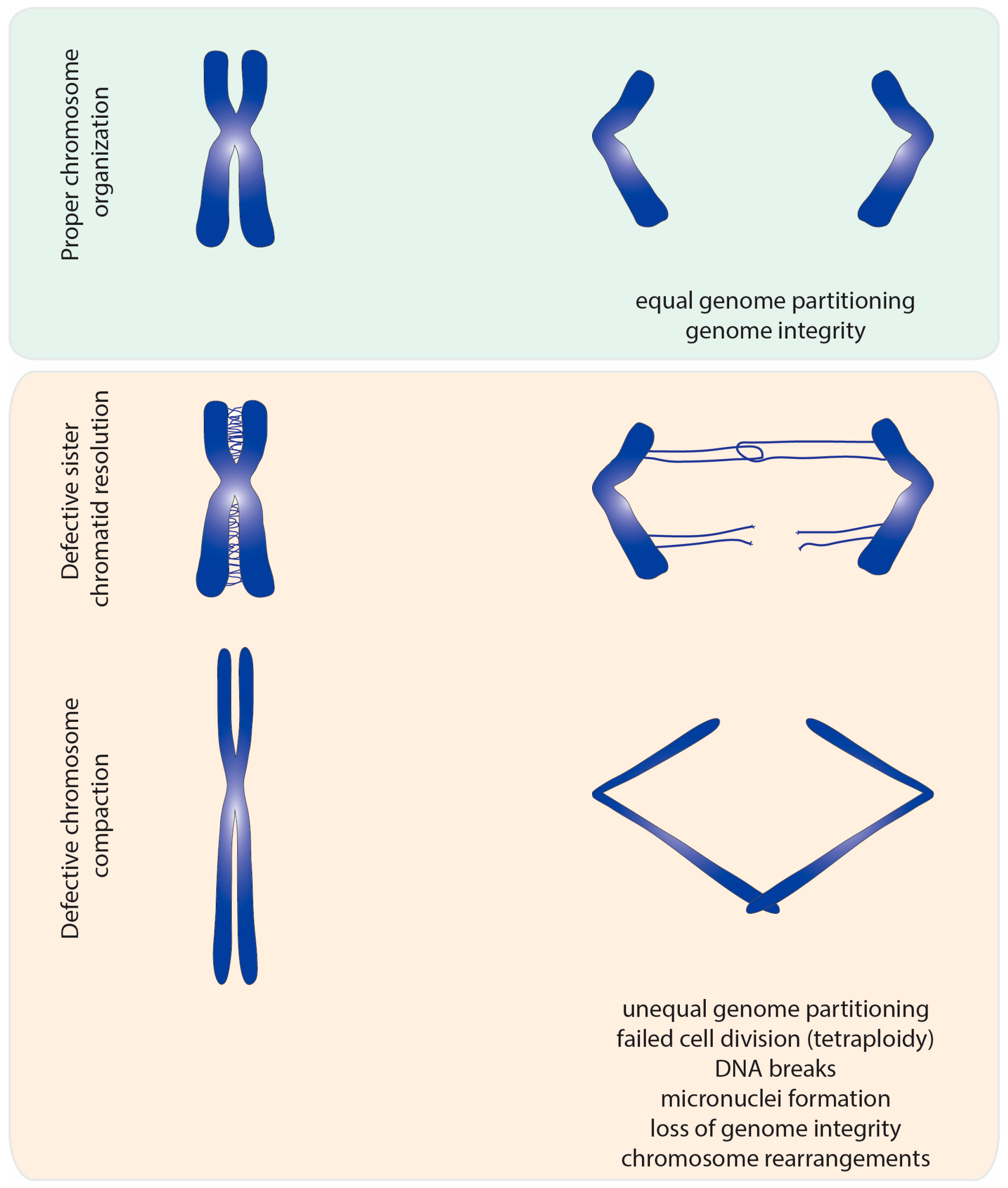
Ijms Free Full Text A Topology Centric View On Mitotic Chromosome Architecture Html

Biologie Kurz Gesagt Teil 1 Chromosomen Und Begriffe Youtube
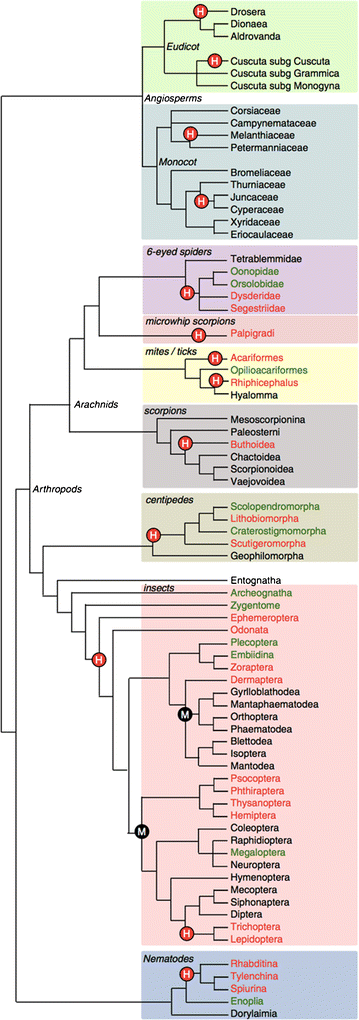
Holocentric Chromosomes Convergent Evolution Meiotic Adaptations And Genomic Analysis Springerlink

Genetik Flashcards Quizlet

Understanding Genetics
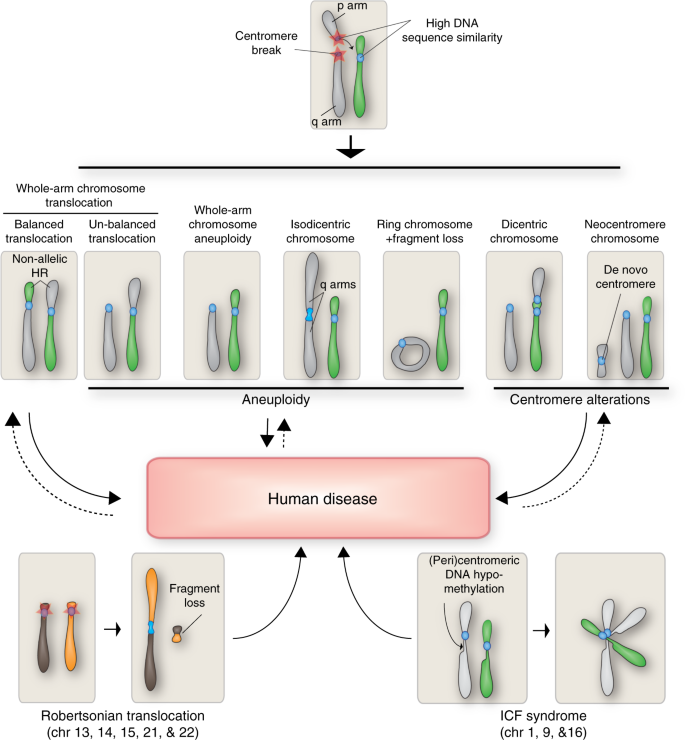
The Dark Side Of Centromeres Types Causes And Consequences Of Structural Abnormalities Implicating Centromeric Dna Nature Communications

Chromosome Wikipedia

Chromosomen Aufbau Und Darstellung Mit Video
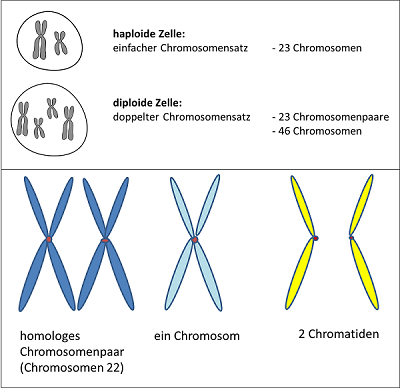
Meiose Reifeteilung Lernen Mit Serlo
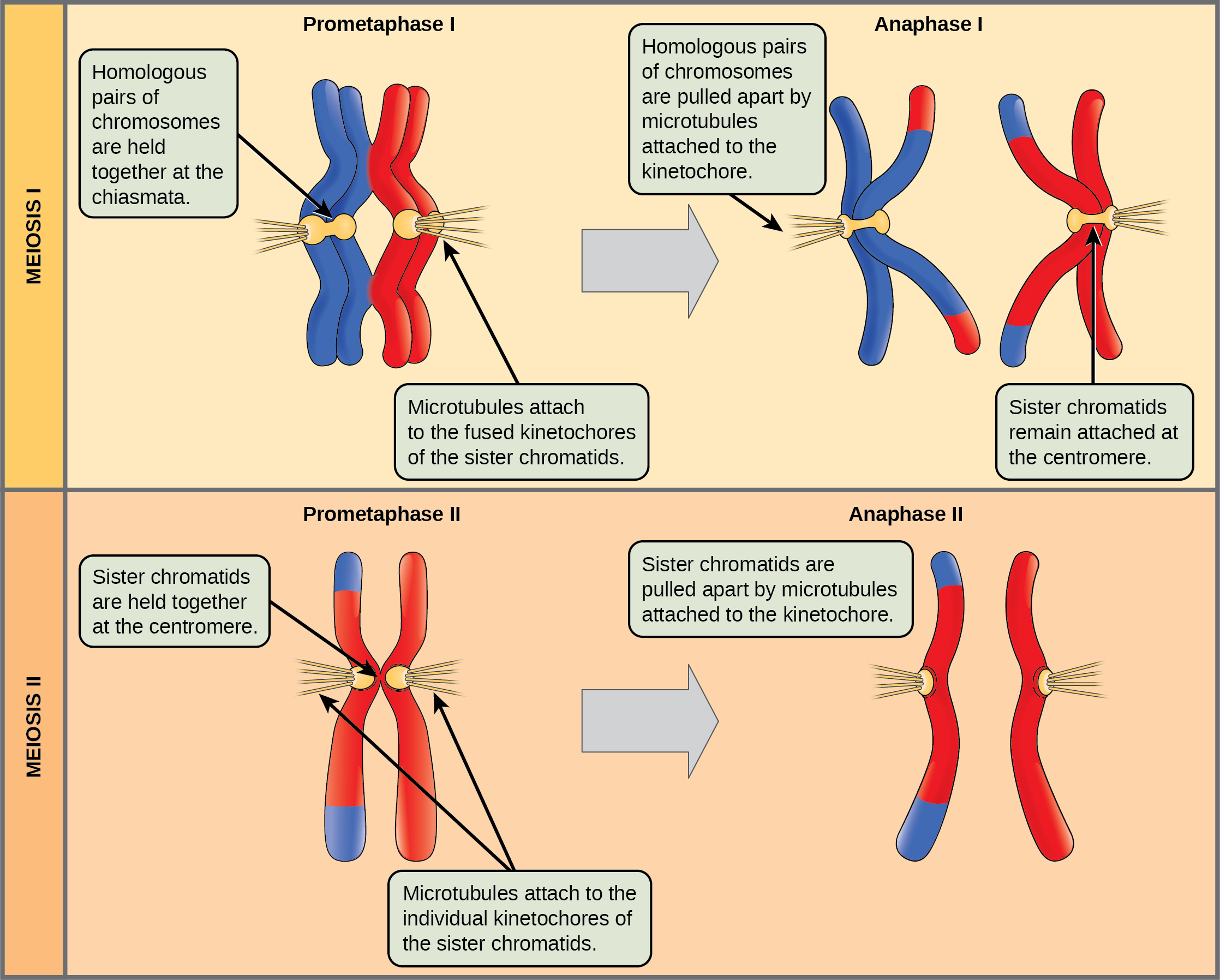
The Process Of Meiosis Biology 2e

Chromosome Abnormalities
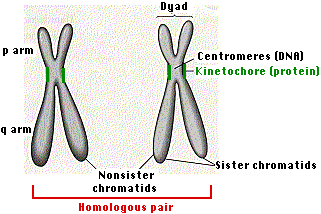
Chromosomes
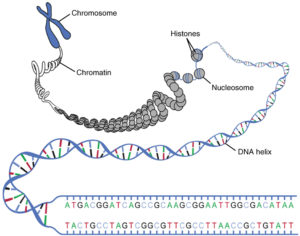
Mars Versus Venus English Part 2 Why Are There Two Sexes Internet Evoluzzer
Q Tbn And9gcravtuflmcaeubzfkfnl0s10rxhagglq3dzty8wqp K9f3zzrye Usqp Cau
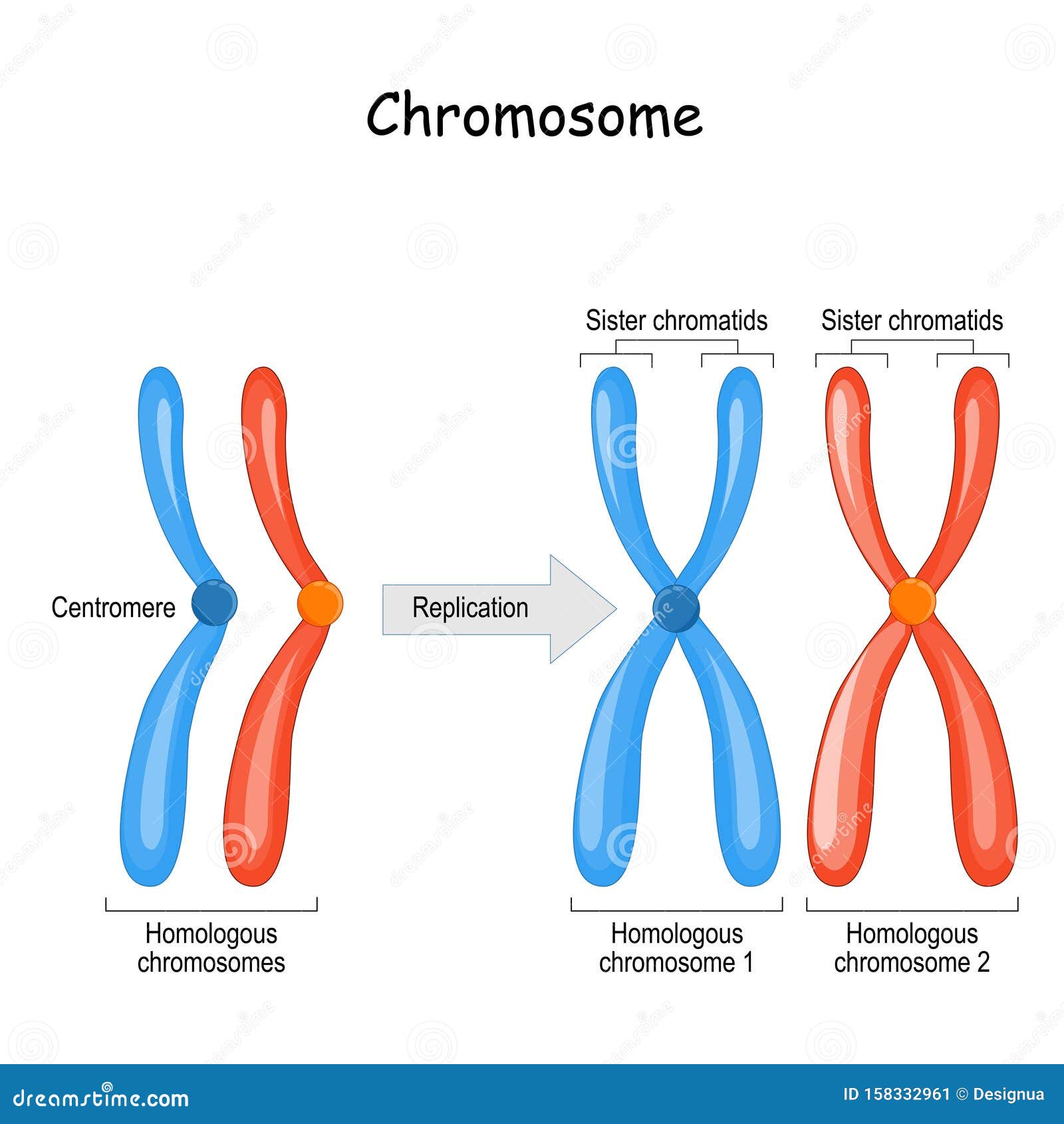
Difference Between Homologous Chromosomes A Pair Of Homologous Chromosomes And Sister Chromatids Stock Vector Illustration Of Genetic Biology

Chromosome Segregation Wikipedia

A Quantitative Map Of Human Condensins Provides New Insights Into Mitotic Chromosome Architecture Biorxiv
How Many Chromatids Does Each Chromosome Have Before S Phase Quora

Homologous Chromosomes Definition Examples Biology Dictionary

Chromosomen Und Chromatin Theoretisches Material Biologie 12 Schulstufe

Chromosomen Und Chromatin Theoretisches Material Biologie 12 Schulstufe
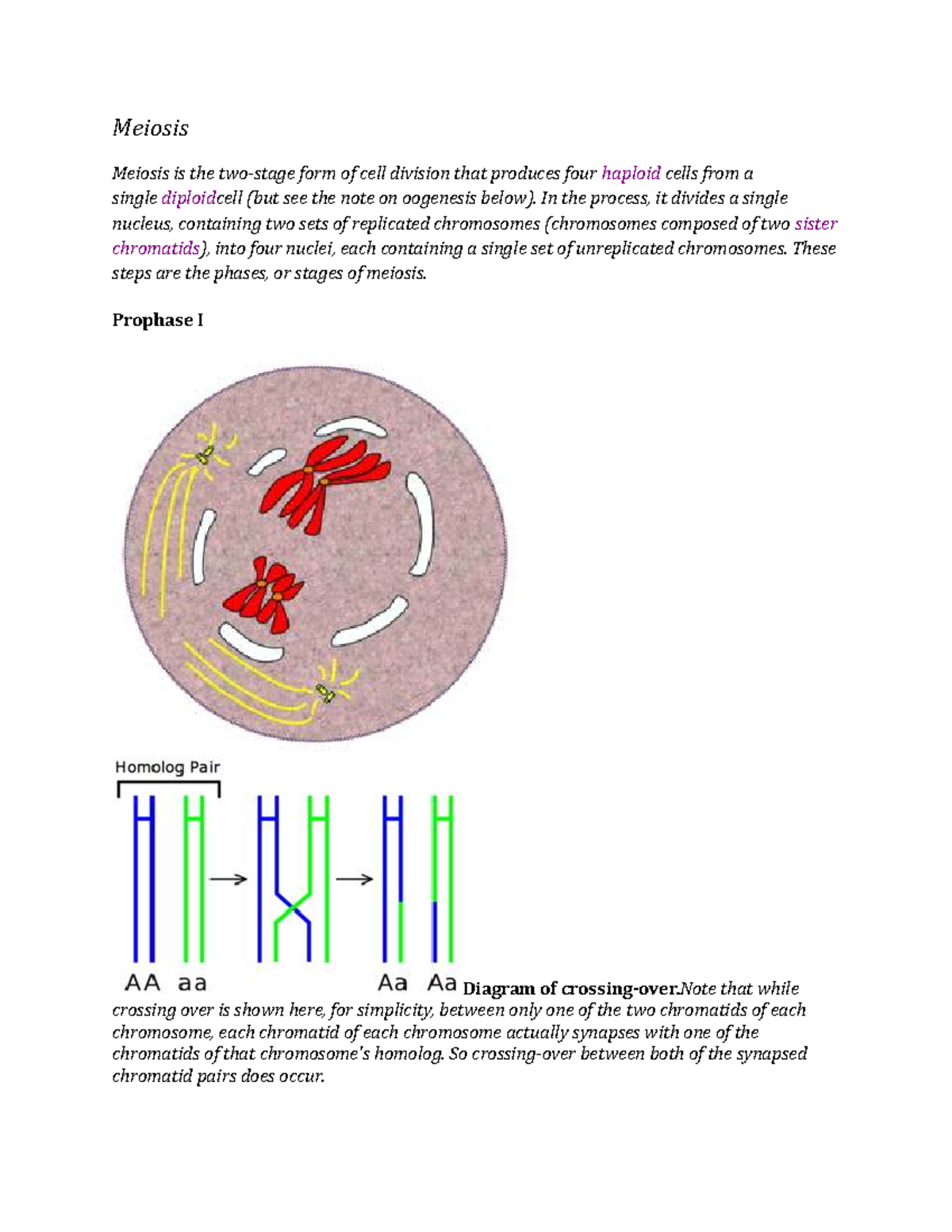
Meiosis 1 B Sc Biotech Bt001 Studocu

What Is A Chromosome Biology Stack Exchange

Chromosomen Und Chromatin Theoretisches Material Biologie 12 Schulstufe

Meiosis Read Biology Ck 12 Foundation
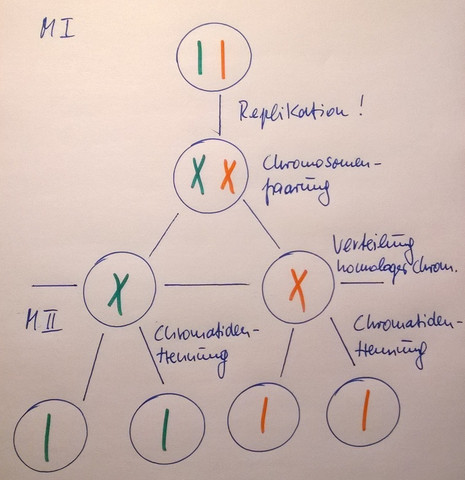
Meiose Wie Kommt Man Auf 46 Chromosomen Wenn Am Ende Der Meiose Nur 23 Ein Chromatidchromosomen Hat Schule Gesundheit Und Medizin Sport

Biology Exams 4 U Chromosome And Chromatid Count In Humans During Mitosis
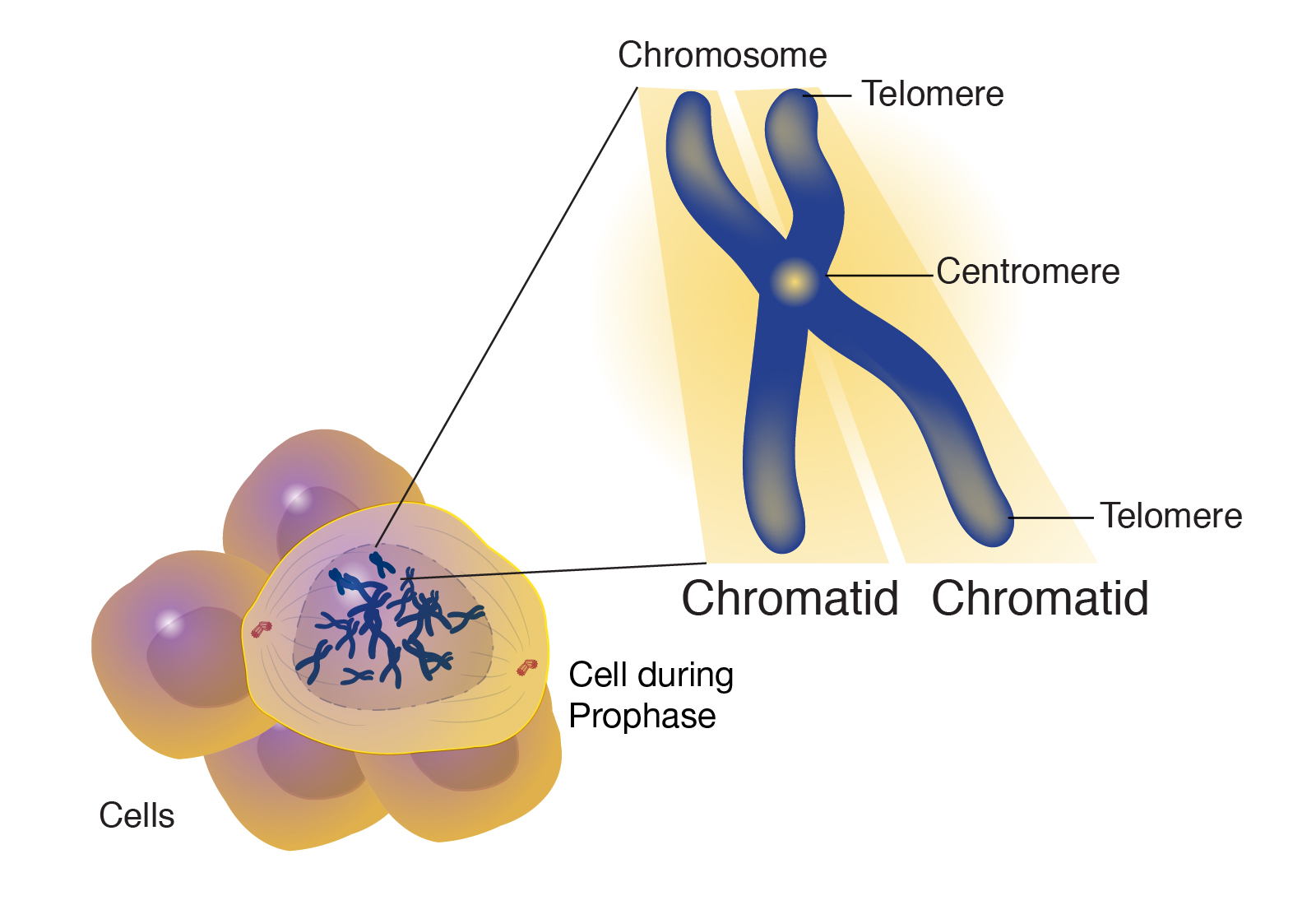
Chromatid

Ring Chromosomes Vicious Circles At The End And Beginning Of Life

Genetics Basics Lesson 5 Meiosis
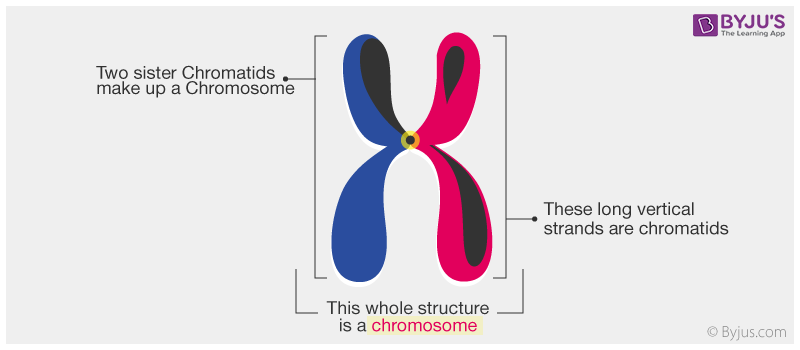
What Is The Difference Between Chromosome And Chromatid
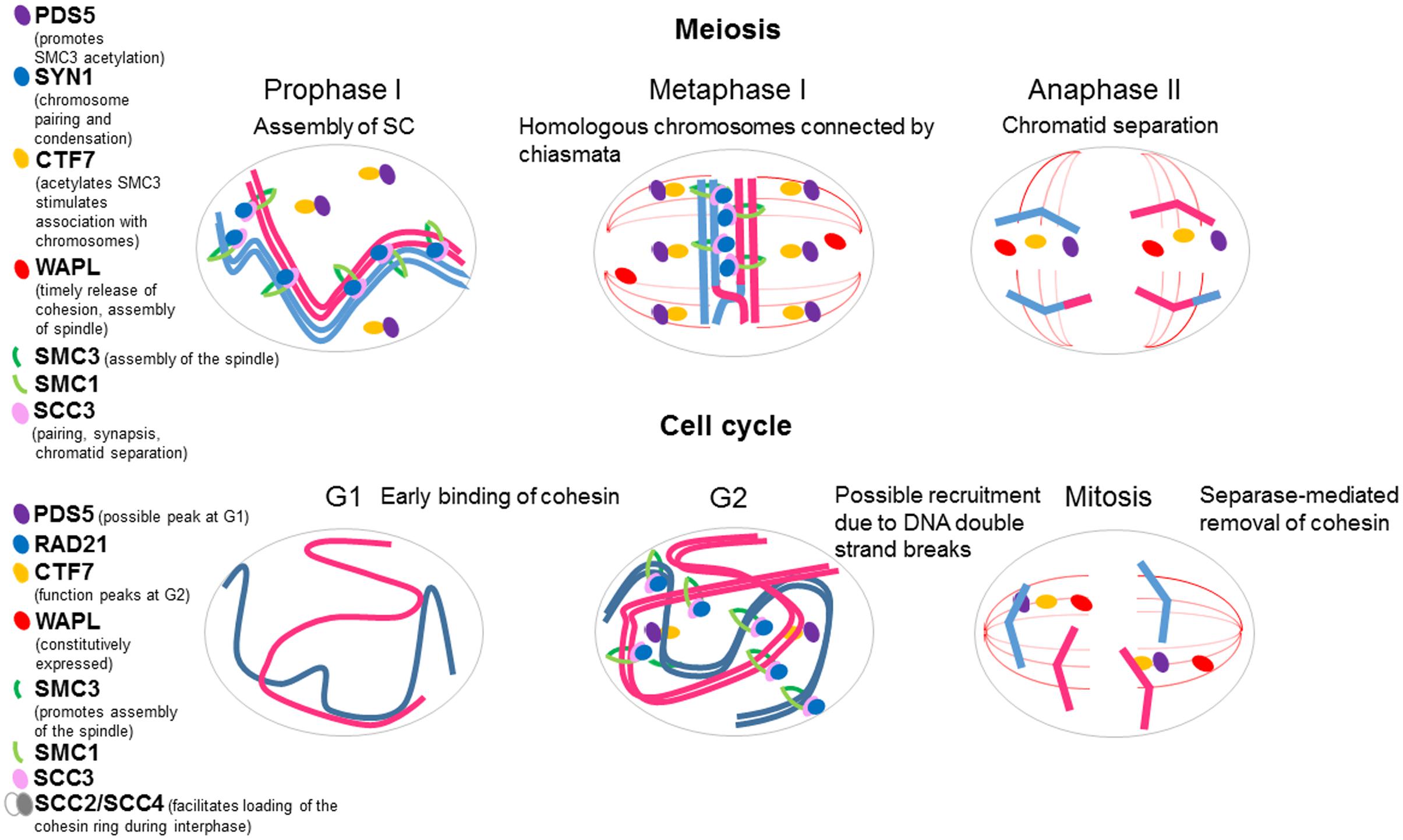
Frontiers In Favor Of Establishment Regulation Of Chromatid Cohesion In Plants Plant Science

Sister Chromatids Definition Concept Video Lesson Transcript Study Com

Unterschied Zwischen Homologen Chromosomen Einem Paar Stock Vektorgrafik Lizenzfrei

Chromosome Behaviour At Meiosis Meiosis Consists Of Two Rounds Of Download Scientific Diagram
What Are The Differences Between Chromosomes Chromatids And Chromatin Quora

Chromatid Biology Britannica
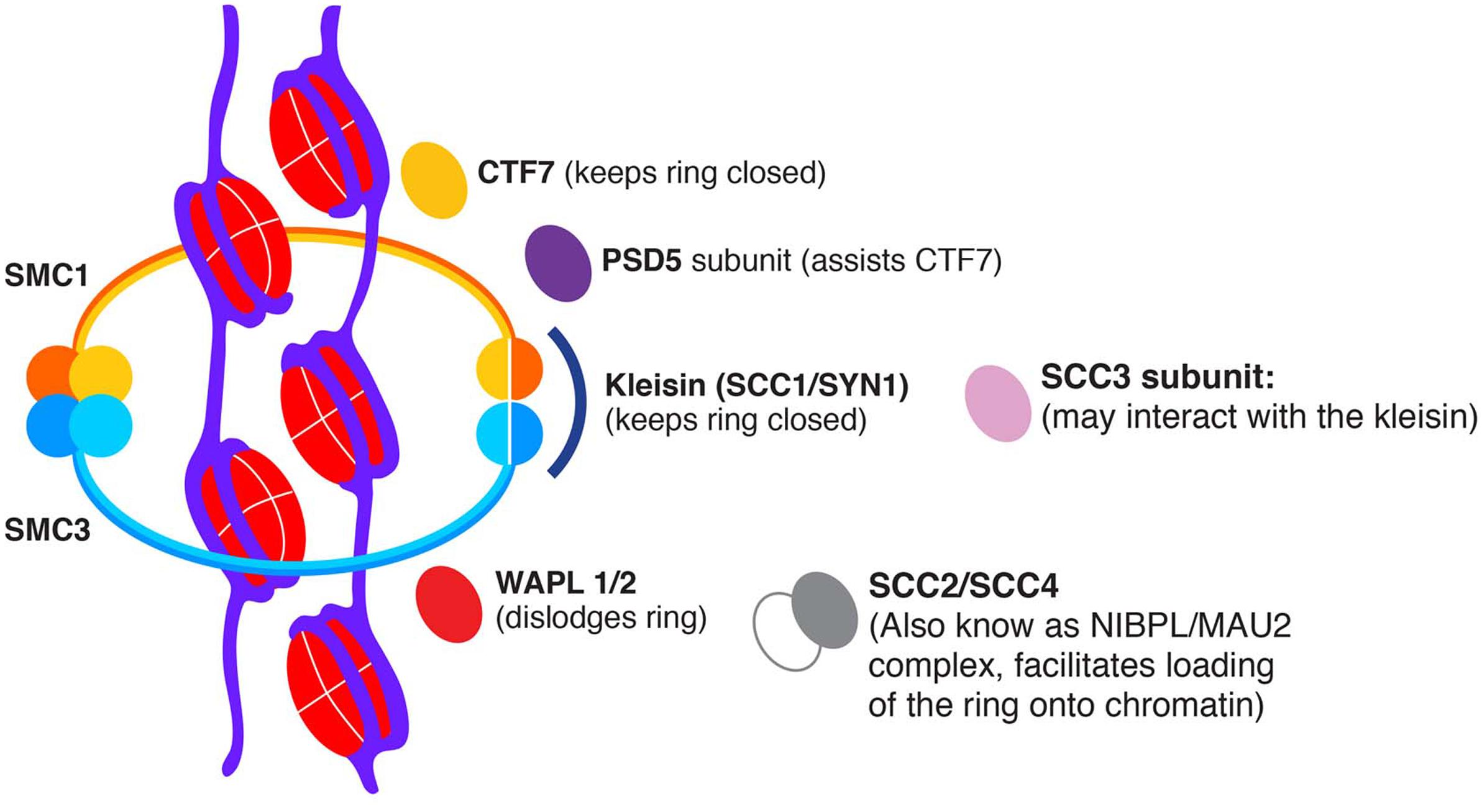
Frontiers In Favor Of Establishment Regulation Of Chromatid Cohesion In Plants Plant Science

Pdf In Favor Of Establishment Regulation Of Chromatid Cohesion In Plants
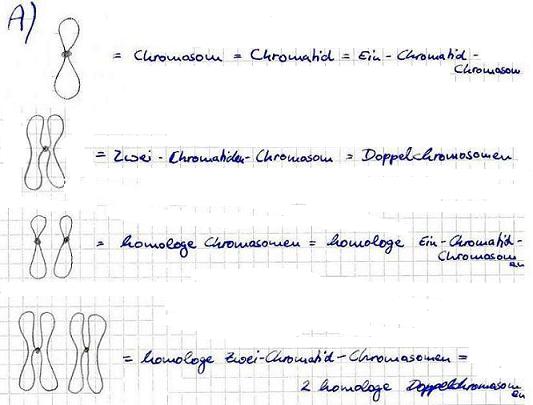
Chromosomen
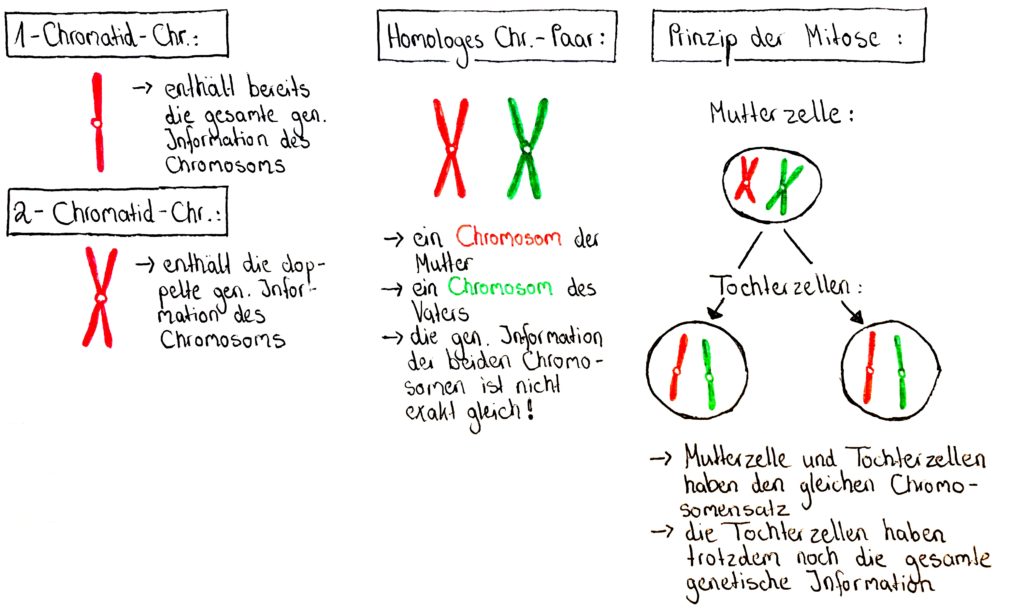
Folge 031 Der Ablauf Des Zellzyklus Genetik Teil 3
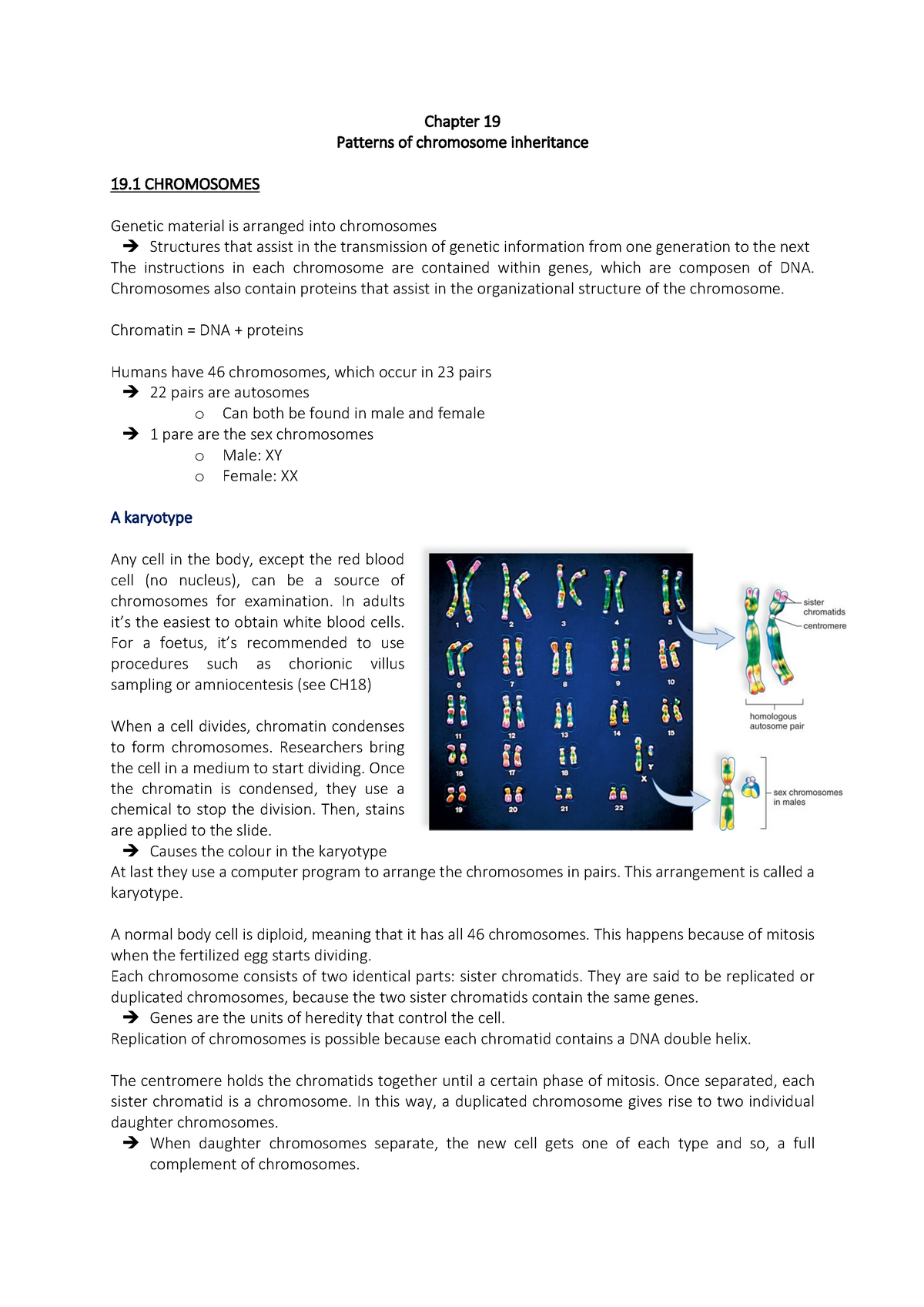
Chapter 19 Samenvatting Human Biology Chapter 19 Patterns Of Chromosome Inheritance 19 Chromosomes Genetic Material Is Arranged Into Chromosomes Structures Studocu
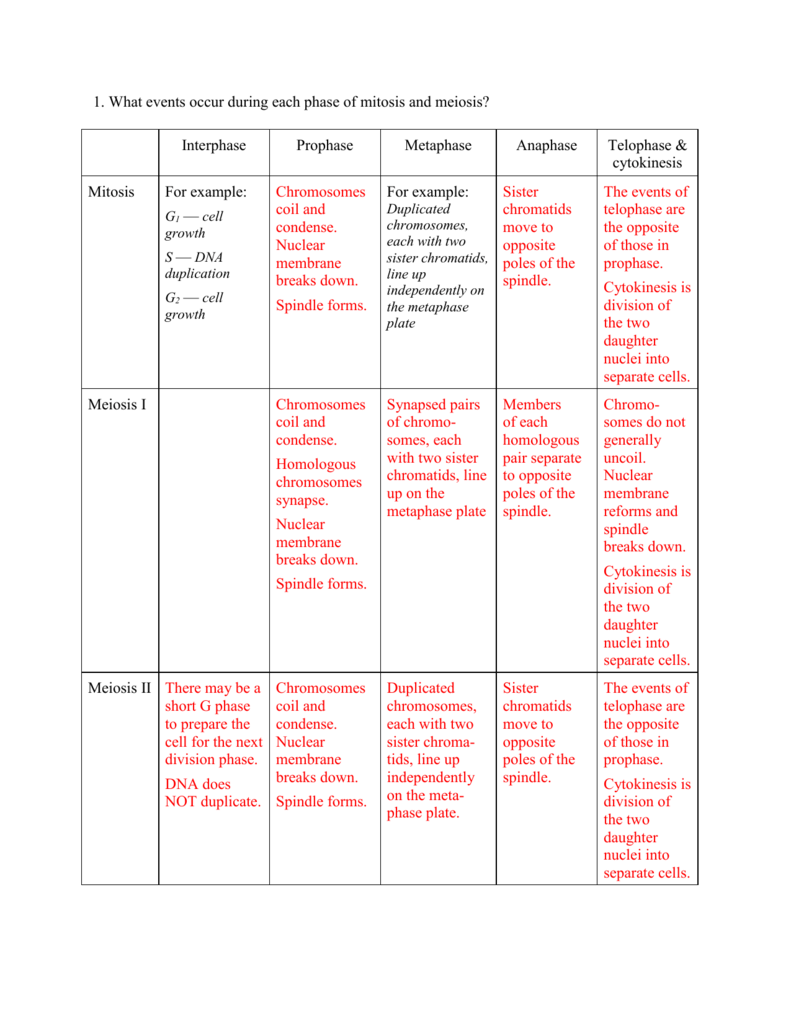
1 What Events Occur During Each Phase Of Mitosis And Meiosis
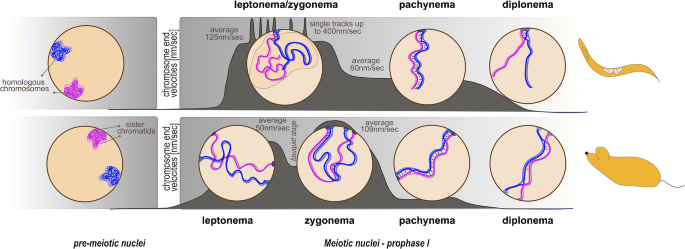
Meiotic Chromosomes In Motion A Perspective From Mus Musculus And Caenorhabditis Elegans Springerlink

Ring Chromosomes Vicious Circles At The End And Beginning Of Life

The Dynamics Of Centromere Motion Through The Metaphase To Anaphase Transition Reveal A Centromere Separation Order Biorxiv

Warum Besitzen Geschlechtszellen Immer Nur Immer Nur 1 Chromatid Chromosomen Schule Gesundheit Und Medizin Biologie
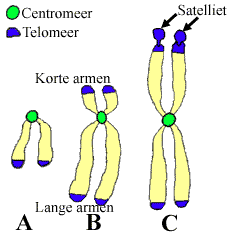
Chromosomes Chromatids

Three Dimensional Positioning And Structure Of Chromosomes In A Human Prophase Nucleus Science Advances

Ijms Free Full Text A Topology Centric View On Mitotic Chromosome Architecture Html

What Is A Chromosome Biology Stack Exchange

What Are The Differences Between Chromosomes Chromatids And Chromatin Quora
Kinetochore Wikipedia
F9ex7dmyqkmspm
Www Longdom Org Open Access Genetic Etiology Of Chromosome 21 Nondisjunction And Down Syndromebirth Aberrant Recombination And Beyond 2472 1115 Pdf
Q Tbn And9gcs9vvudbqqvyoblfkck9cqyibmuxwadnbhqmpj0ib6vz3gvau9m Usqp Cau

A Genetic Mechanism Implicates Chromosome 11 In Schizophrenia And Bipolar Diseases Genetics
Centromere Proteins Research Tools Creative Biomart Creative Biomart

Mitotic Chromosome Mechanics How Cells Segregate Their Genome Trends In Cell Biology
F9ex7dmyqkmspm
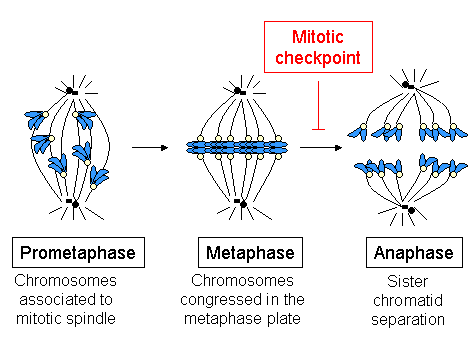
Chromosome Structure And Numbers Review Article Khan Academy
Does A Chromosome Have One Chromatid Or Two Chromatids Quora
Q Tbn And9gcst6ylr9lv8qd Irhakisjndoyn 312f5dbowhzewvbvawgwqm4 Usqp Cau

What Are Chromosomes
Chromosomen

Ijms Free Full Text A Topology Centric View On Mitotic Chromosome Architecture Html

Does A Chromosome Have One Chromatid Or Two Chromatids Quora
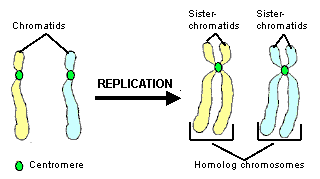
Chromosomes Chromatids

Mitotic Chromosome Mechanics How Cells Segregate Their Genome Sciencedirect
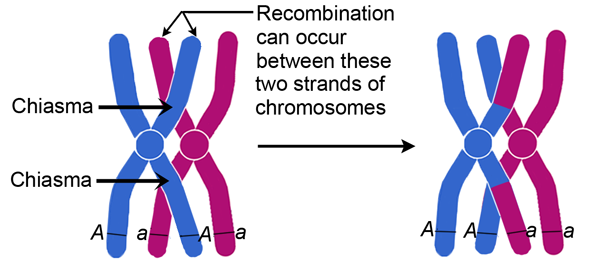
Life Sciences Cyberbridge

Understanding Genetics
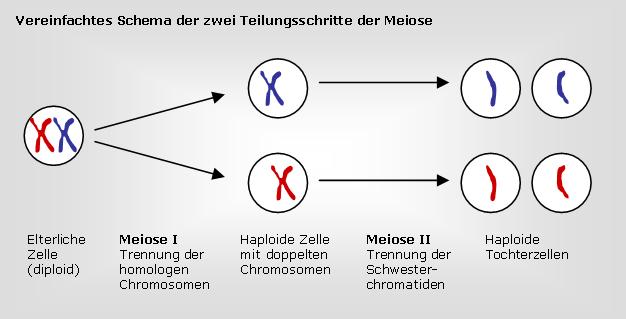
Ngfn

Chromosomen Und Chromatin Theoretisches Material Biologie 12 Schulstufe
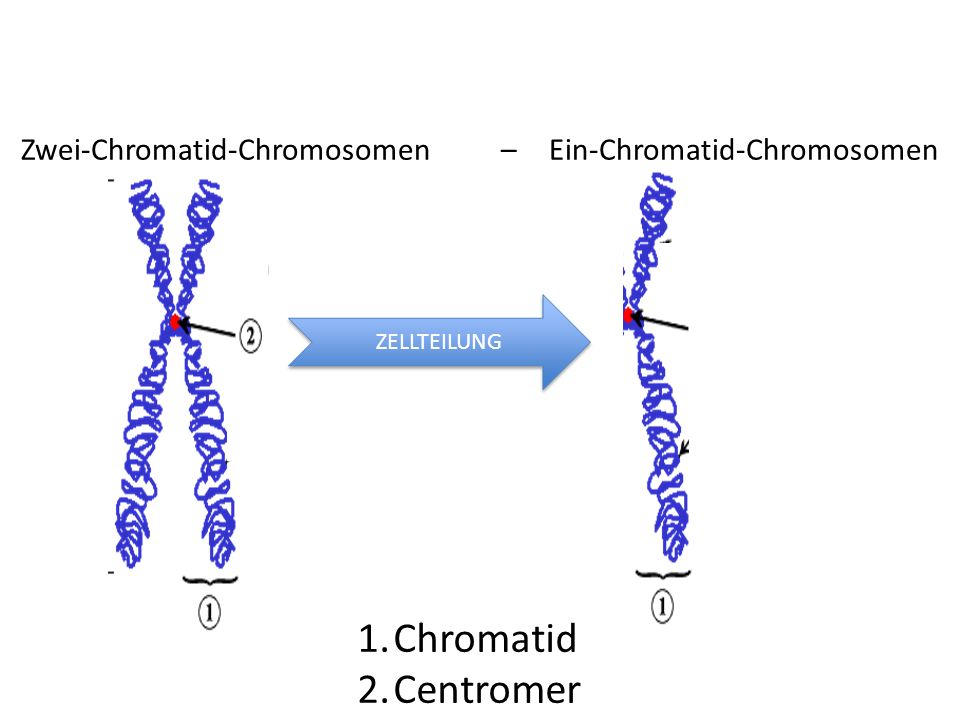
Book Textbook Of Stroke Medicine 09
How Many Dna Molecules And Genes Does A Single Chromosome Contain Quora

Sister Chromatids Definition Concept Video Lesson Transcript Study Com

Synapsis Wikipedia
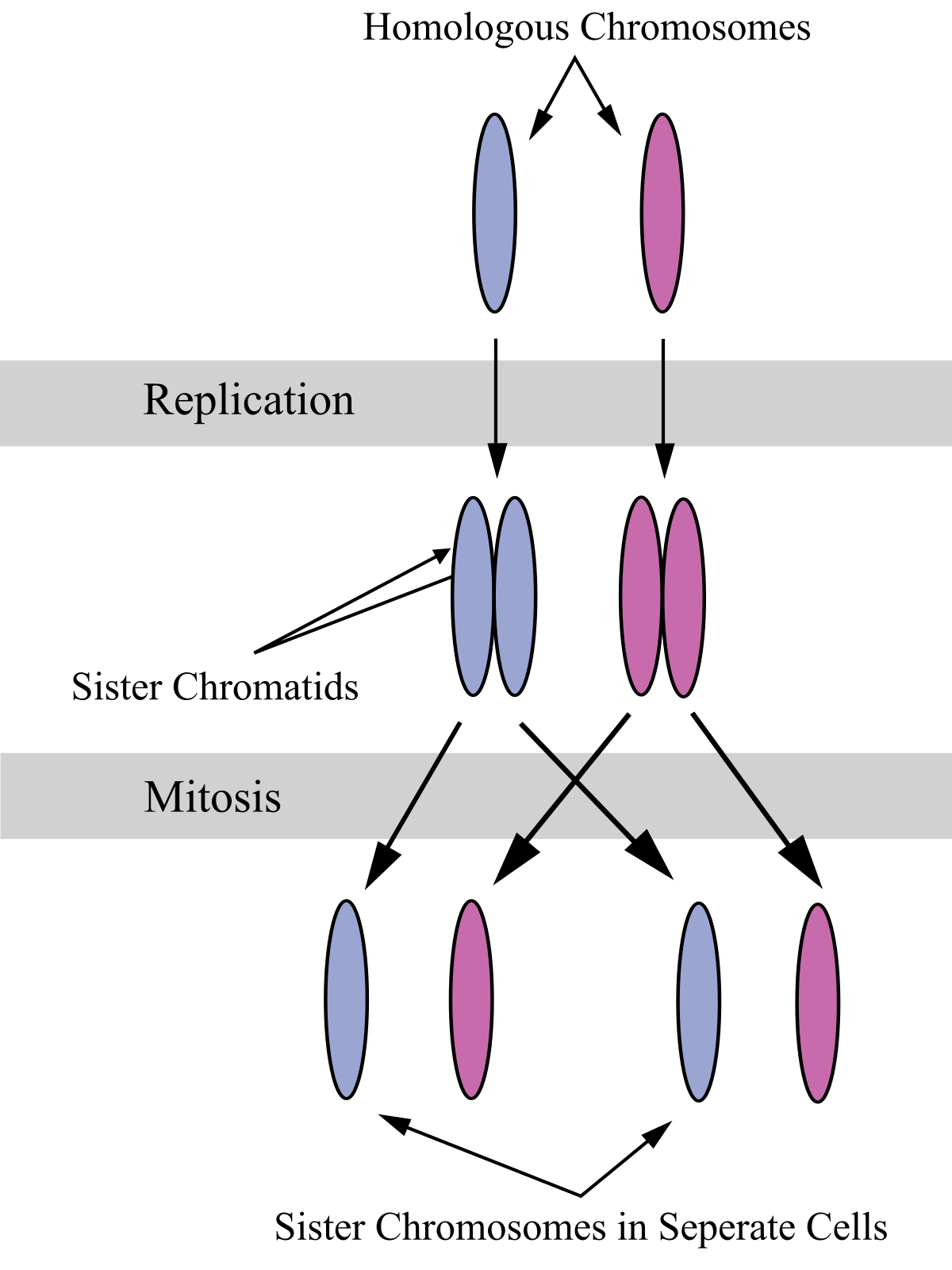
Sister Chromatids Wikipedia
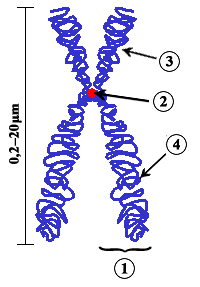
Chromosome Regions Wikipedia
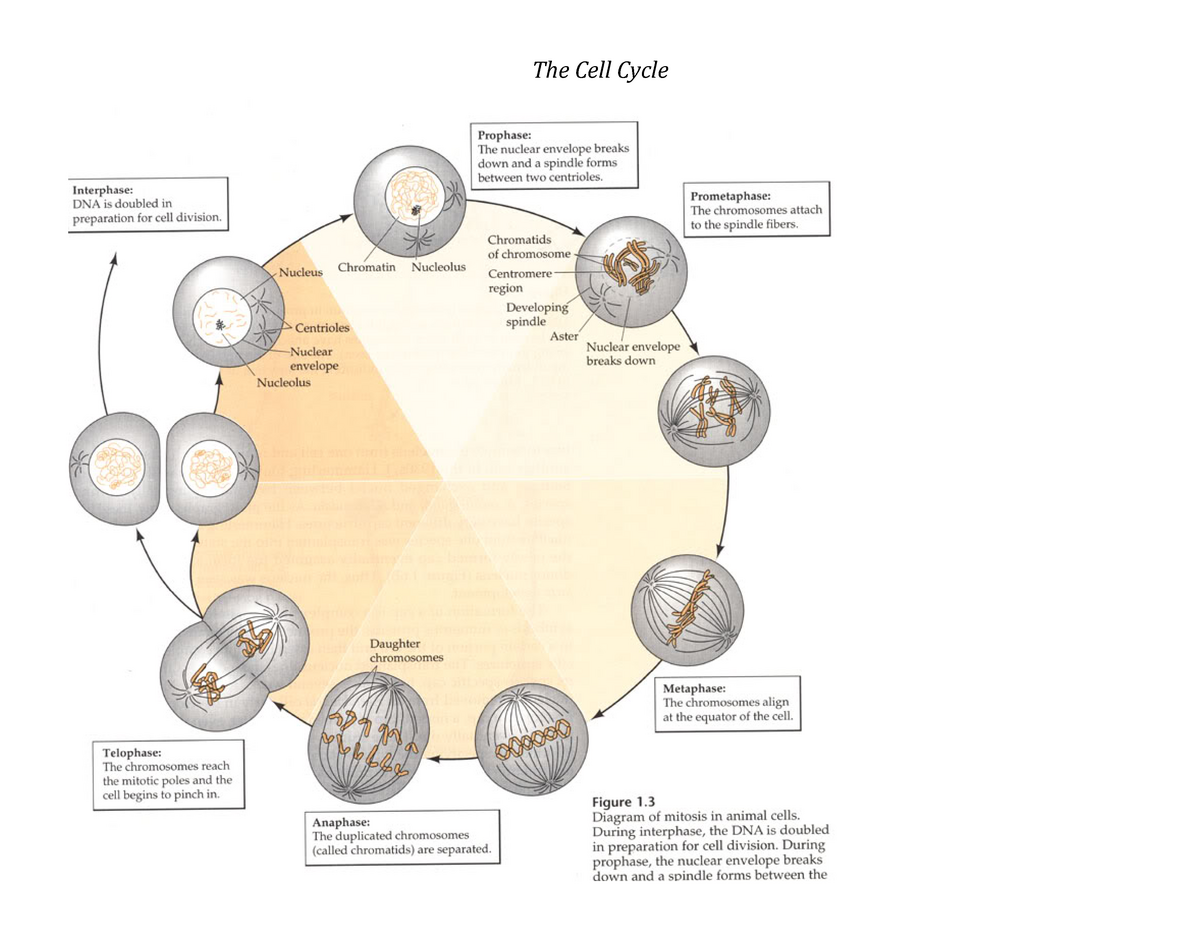
The Cell Cycle Review Bioa 1002 Dal Studocu

Mechanisms Of Genomic Instability In Breast Cancer Trends In Molecular Medicine

Homologous Chromosome Wikipedia

Chromosome Breakage An Overview Sciencedirect Topics

Genetic Diagnosis Of Subfertility The Impact Of Meiosis And Maternal Effects Journal Of Medical Genetics



